The immune system is your body’s defense system. It protects you from things that can make you sick, like germs (bacteria, viruses, and fungi) and harmful substances. Think of it as an army that fights off invaders trying to attack your body.
Parts of the Immune System:
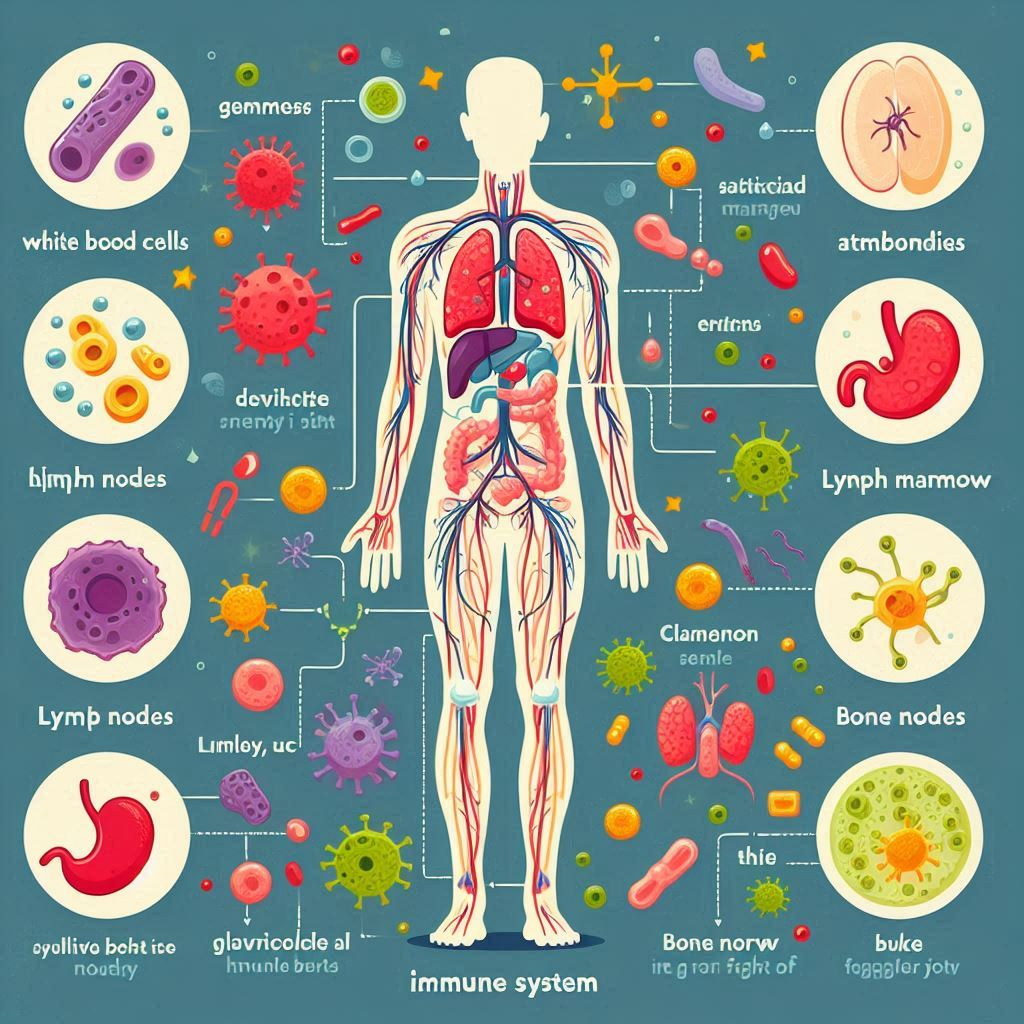
- White Blood Cells: These are the soldiers of the immune system. They move around your body, looking for invaders. When they find germs, they attack and destroy them. There are different types of white blood cells, each with a special job.
- Antibodies: These are special proteins made by your body. They recognize and attach to germs, marking them for destruction. It’s like putting a ‘target’ on the invaders so your body knows what to attack.
- Lymphatic System: This is a network of tubes and nodes (small, bean-shaped structures) throughout your body. It helps move white blood cells and other immune cells around. Lymph nodes are like checkpoints where germs are trapped and destroyed.
- Bone Marrow: This soft tissue inside your bones is essential for producing new blood cells, including white blood cells, which are crucial for your immune system. Bone marrow continuously generates these cells to replace old ones and maintain a healthy blood supply for fighting infections and supporting overall health.
- Spleen: The spleen is an organ that filters your blood. It removes old or damaged cells and helps produce white blood cells that fight infection.
- Skin and Mucous Membranes: Your skin and the lining inside your nose and mouth act as barriers. They’re like walls that keep germs out of your body. Mucus traps germs, and sneezing or coughing helps expel them.
How the Immune System Works:
- Recognize Invaders: When germs such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi enter your body, your immune system immediately identifies them as foreign substances. It detects these invaders through specialized cells and proteins that recognize patterns unique to pathogens. This recognition is crucial for initiating a targeted immune response. By distinguishing between harmful invaders and your own healthy cells, the immune system effectively mobilizes its defense mechanisms to protect your body from infections and diseases.
- Attack Invaders: Once identified, the immune system sends white blood cells to attack and destroy the invaders. This process can cause inflammation, like redness and swelling, as your body fights back.
- Remember Invaders: After an infection or exposure to harmful germs, your immune system retains a memory of these invaders. It creates a record of the specific germs it has encountered and fought off. This memory enables the immune system to recognize and respond more swiftly and effectively if the same germ attempts to invade again, providing enhanced protection and a quicker defense.
Why the Immune System Is Important:
- Protection: The immune system plays a crucial role in maintaining your health by fighting off harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. It identifies and attacks these disease-causing threats to prevent infections and illnesses, helping you stay well and resilient.
- Healing: The immune system is vital for recovery, as it helps your body heal after injuries or illnesses. It not only fights off pathogens but also promotes tissue repair and regeneration. By mobilizing immune cells and releasing healing factors, it supports a faster and more effective recovery process.
- Allergies and Autoimmune Diseases: Sometimes, the immune system can overreact to harmless things like pollen (causing allergies) or mistakenly attack the body’s own cells (causing autoimmune diseases).
How to Keep Your Immune System Strong:
- Eat Healthy: Incorporating a variety of foods rich in essential vitamins and minerals, such as fresh fruits, leafy greens, whole grains, nuts, and seeds, can greatly enhance your overall health. These nutrient-dense foods provide antioxidants, fiber, and other vital nutrients that support the immune system, boost energy levels, improve digestion, and promote a strong, balanced body.
- Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, cycling, or strength training, plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy immune system. Exercise increases circulation, helps flush out toxins, and reduces inflammation, which supports immune function. It also helps regulate stress hormones, improves mood, and enhances overall physical and mental well-being.
- Sleep Well: Adequate sleep is essential for your body’s well-being. It allows the immune system to function optimally by supporting its ability to fight off infections and diseases. Quality sleep also helps repair tissues, regulate stress hormones, and maintain overall health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is vital for maintaining overall health. Proper hydration supports all bodily functions, including the immune system, by ensuring efficient nutrient transport, toxin removal, and cellular health. Water also helps maintain optimal body temperature and supports digestion, making it essential for a well-functioning immune response and overall vitality.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can significantly weaken the immune system, impairing its ability to fight infections and maintain overall health.
The immune system is like your body’s personal superhero, always on guard to protect you from harm. It works tirelessly to detect and combat harmful invaders like bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. With a network of specialized cells, tissues, and organs, the immune system identifies threats, launches targeted attacks, and remembers past invaders to respond more effectively in the future. By maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you support this vital defense system in keeping you safe and healthy.








Leave a Reply